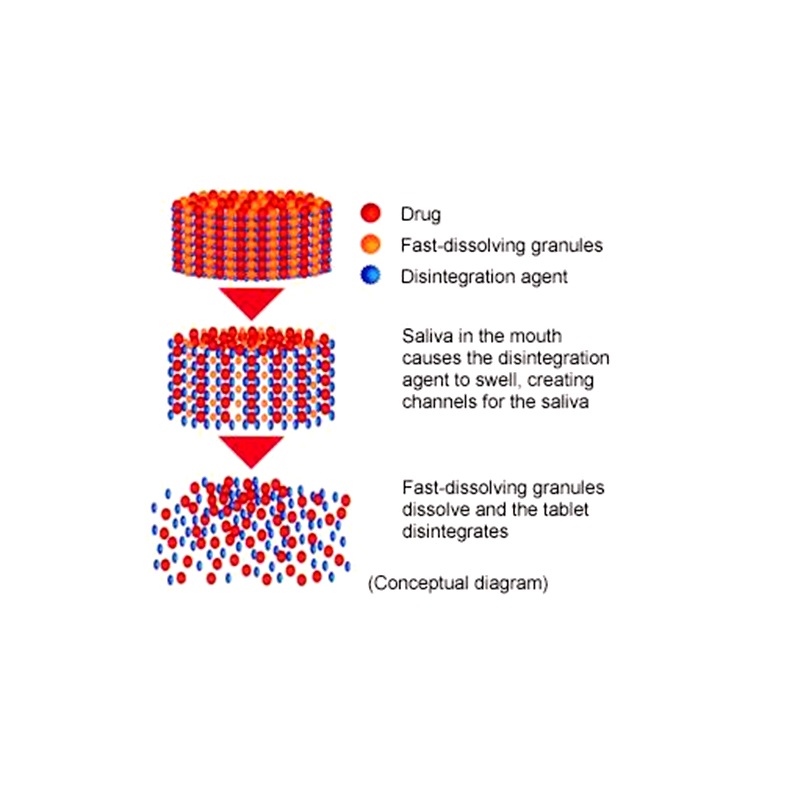
❖ Introduction:
The Fast DDS was designed to provide patients with a more conventional method of taking their drugs. Patients of all ages have dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, as a result of physiological changes; this is especially true for the young and elderly. Solid dose forms that are soluble, disintegrable, or suspended by saliva in the mouth for easy swallowing are very beneficial for patients who are younger, older, or prefer easily swallowable forms. This pill dissolves rapidly on the tongue, releasing the drug, which then dissolves or diffuses in the saliva.
Fig.1.1. Concept of fast dissolving tablet
Recent studies have focused on pharmaceutical preparations for the elderly with the goal of improving their quality of life and adherence to treatment. A visually appealing dosage form and patient-centered pharmaceutical preparation is a tablet with a rapid rate of disintegration in saliva.
Rapid dissolving tablets are a popular and growing medicine delivery technology. Since these dose forms boost a drug’s tolerability and bioavailability while blocking first-pass metabolism, they are also frequently used for treatments with limited bioavailability.
The dissolving pills are attracting the interest of many researchers. Many elderly people have difficulty swallowing tablets, powders, or pills. It is believed that the dissolution or disintegration of these pills in the oral cavity may alleviate this problem without the need for water. Saliva facilitates the smooth passage of the dissolved substance down the throat, making it easy to swallow and chew for even individuals who have swallowing difficulties.
There are two types of dispersible pills that must be distinguished. One tablet formulation readily creates dispersion in water that is easy for the patient to take, while one dose form dissolves instantaneously in the mouth and can be eaten without the need for water.
1.2 Criteria for Fast dissolving DDS: –
Fig. 1.2 Criteria for Fast Dissolving DDS
Instead of needing to be swallowed with water, tablets should dissolve & disinter-grate in the mouth within a matter of seconds. Taste-masking protocols. Be lightweight and invulnerable to breakage. Feel pleasant when speaking. Leave as little & no residue in the mouth after oral administration. Display little sensitivity to temperature and humidity levels in the environment, and tablet to be produced at a minimal cost using common processing and packaging equipment.
1.3 Salient Features of Fast Dissolving DDS:
Simple administration to patients who have trouble swallowing, such as the elderly, stroke victims, bedridden patients, renal failure patients, and patients refusing to swallow in pediatric, geriatric, and mental health settings. One very useful aspect for people who are on the road and don’t always have access to water is that the dosage form can be swallowed without water. Certain drugs from the mouth, throat, & oesophagus are absorbed when saliva descends into the stomach. This accelerates the drug’s breakdown and absorption so that it acts sooner rather than later. A medication’s bioavailability is improved in these circumstances. Pre-gastric absorption can improve clinical performance by minimizing side effects and reducing dosage while increasing bioavailability. Good tongue feel qualities can help change the perception that medication is a bitter tablet, especially in younger patients.
The standard formulation can be administered orally without physical blockage, which reduces the risk of suffocation and choking and enhances safety. Because the medication is supplied in a solid dose form until it is digested, these tablets have a faster dissolving and disintegration rate, which increases the bioavailability of the drug, especially for insoluble & hydro-phobic pharmaceuticals. This amalgamates the advantages of a liquid dosage form regarding bioavailability with that of a solid dosage form concerning stability.
1.3.1 Advantages of Fast Dissolving Tablet:
Fast dissolving tablets (FDTs) are a type of solid unit dose form that allows for high drug loading and precise administration. They are an excellent alternative to conventional tablets and is suggested for dosage for both pediatric and geriatric patients.
As soon as patient takes it, it activates immediately; it penetrates into oral cavity quickly, melts quickly, acts quickly when it comes into touch with saliva.
Pre-gastric absorption affects patient compliance and clinical reports by changing the bioavailability of drugs and lowering dose.
Fast-dispersing tablets can be taken anywhere and at any time without the need to swallow water.
Because of this, they are an easy option for patients who are on the road and for responsible people who do not always have access to water, which increases patient compliance.
They are simple to administer to geriatric, pediatric, resistant, and dysphasic individuals because of their solid unit dose form structure.
Fast-dissolving tablets consist of fewer leaves and dissolve entirely in the mouth, leaving no trace, resulting in an improved and pleasant mouthfeel.
Because fast-disposing tablets are less sensitive to outside influences, they offer great stability.
They come in simple blister packing & don’t need additional expensive packaging, making fast-dissolving tablets inexpensive.
Rapid dissolving pills present emerging commercial prospects such as product diversification, line extension, life cycle management, and advertising.
Fast-dissolving tablets are economical as they do not necessitate expensive ingredients.
Natural polymers can be packaged in simple blister packs and are readily accessible, affordable, and require no special packaging materials when used as excipients.
They are a versatile technology because they are utilized in production of prescription, over-the-counter, and veterinary drugs.
They are also conveniently portable due to their solid dosage form, resistance to environmental changes, and lack of water requirement.
1.4 Limitations of Mouth Dissolving Tablets:
The mechanical strength of the pills is usually insufficient. As such, handling needs to be done with caution. Incorrect tablet formation could result in a bad taste and/or grittiness in the tongue.
1.5 Prerequisite of fast-disintegrating tablets:
The following conditions must be met in order for fast-dissolving pills to work: The tablet must disintegrate and spread in the mouth without the need for water. It can hold a lot of drugs. It ought to have the greatest sensory effect and blend well with excipients and flavor masking agents. Leave minimal to no residue in the event of administration. It should be able to withstand formulation processes as well as feasible. It should be steady within the range of temperature and humidity. It should be adaptable and work with current processing and packing machinery. It should be produced at a reasonable cost.
1.6 Suitability of drugs for fast disintegrating tablets:
While selecting the medication, excipients, and formulation method for a particular FDT, several factors should be taken into account. The following is a list of these in order:
- Digs should not be used for extended periods of time as FDT candidates. It is not recommended to take medications like clopidogrel, which have an extremely terrible taste.
- People with Jorgen’s syndrome and those with decreased salivary production are not suitable candidates for the FDT dosage form. It is not appropriate to take medications with frequent dosing requirements and a relatively short half-life.
- People on anti-cholinergic medication shouldn’t take part in FDT. Medicines like buspirone, apomorphine, and selegiline that display altered pharmacokinetic behavior when packaged in a dose form other than their customary dosage form shouldn’t be used. Medications that are well absorbed in pre-gastric and oral areas and that generate a large amount of harmful metabolites in GIT and first-pass metabolism are good choices. It is believed that medications that can cross the upper GIT & oral mucosal epithelial cell lining would be a good fit for FDT.
1. 7 Drugs which can be integrated in the FDT
Drugs of all kinds are being added to FDTs.
| S.No. | Category | Drug |
| 1 | Analgesics and Anti-inflammatory agents | Piroxicam, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Sulindac, Phenylbutazone, Naproxen, Indomethacin. |
| 2 | Antiepileptic | Carbamazepine, Methsuximide, Phenytoin, Primidone, Phenobarbitone, Valproic acid, |
| 3 | Antifungal agents | Clotrimazole, Amphotericin, Griseofulvin, Ketoconazole, Miconazole, Nystatin, Terbinafine, Fluconazole |
| 4 | Antimalarial | Chloroquine, Mefloquine, Proguanil, Pyrimethamine |
| 5 | Antigout agents | Allopurinol, Probenecid, Sulphinpyrazone |
Table 1.1: Various drug that is used in fast dissolving tablets
1.8 Excipients required in formulating FDTs:-
Depending on the kind of medicine, a lubricant & optional swelling agent, a diluent/bulking agent, a super-disintegrant, a permeabilizing agent, sweeteners, and flavouring agents are among the excipients used in FDTs. The table below provides names of excipient classes along with their percentages.
| S.No | Name of the Excipients | % used |
| 1 | Superdisintegrants | 1-15 |
| 2 | Binder | 5-10 |
| 3 | Antistatic agent | 0-10 |
| 4 | Diluents | 0–85 |
Table 1.2: Names & Weight % of Various Major Excipients
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the exploration of fast-dissolving drug delivery systems at IIMT University in Meerut marks a significant stride towards revolutionizing pharmaceutical sciences. The journey through this research has shed light on the potential of FDDDS to address critical challenges in drug administration, ultimately improving patient outcomes. The merits of fast-dissolving drug delivery systems, such as enhanced bioavailability, rapid onset of action, and increased patient compliance, have been underscored throughout our investigation.
The synergy of cutting-edge technologies and pharmaceutical sciences at IIMT University has paved the way for the development of novel formulations capable of meeting the evolving needs of modern healthcare. Our research journey underscores the interdisciplinary nature of pharmaceutical sciences, involving pharmacology, formulation development, and material sciences. The collaborative efforts of researchers, faculty members, and students at IIMT University have been instrumental in pushing the boundaries of drug delivery systems. As we move forward, it is essential to recognize the potential of FDDDS in providing solutions to diverse healthcare challenges. Continued research and development in this field hold the promise of not only optimizing drug therapy but also contributing significantly to the pharmaceutical industry’s growth.
Author: Mr. Satya Prakash,
Assistant Professor, SoPS.
To learn more about the FDDDS, click here: