❖ Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent but frequently misconceived hormonal disorder that predominantly affects women of reproductive age. It encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, often exerting a profound influence on a woman’s physical and emotional health. This comprehensive guide is dedicated to elucidating the root causes, manifestations, and potential remedies for PCOS. Through the dissemination of information and provision of support, our goal is to equip women with the tools they need to gain a deeper understanding of this condition and assert greater agency over their well-being.
❖ Understanding PCOS
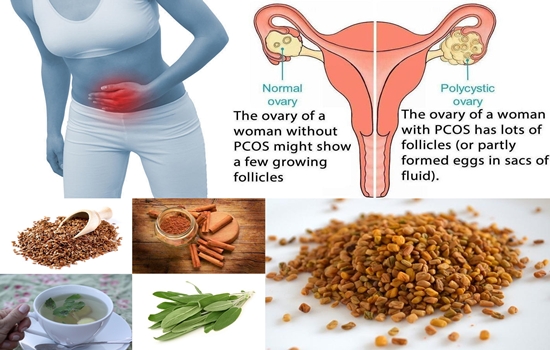
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, abbreviated as PCOS, is a complex endocrine disorder that affects individuals with ovaries, primarily women of reproductive age. PCOS gets its name from the appearance of the ovaries in affected individuals, which may have small cyst-like structures. However, these “cysts” are not true cysts but rather small, undeveloped follicles containing eggs.
❖ Causes of PCOS
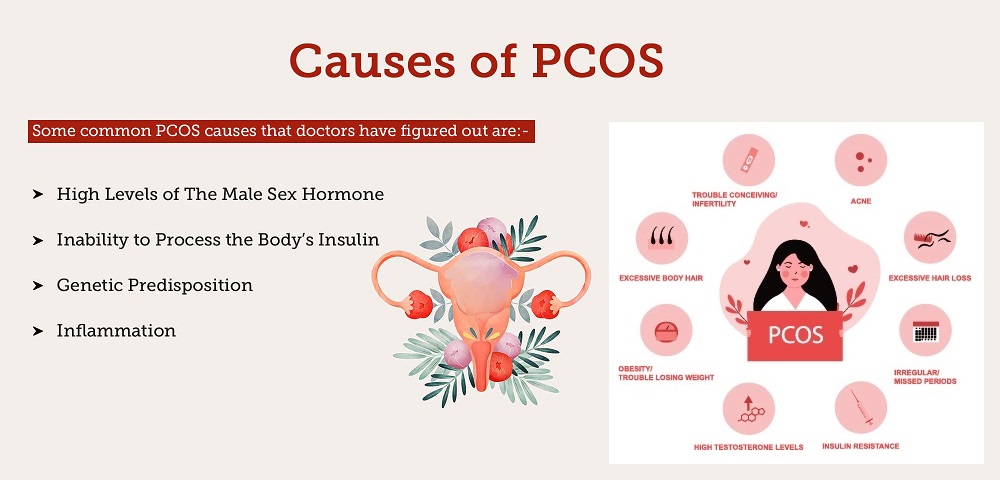
Although the precise origin of PCOS remains elusive, it is generally thought to emerge from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences:
- Genetic Factors:
There is a strong genetic predisposition to PCOS. Women with a family history of PCOS are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Specific genes associated with hormonal regulation and insulin resistance may contribute to the development of PCOS.
- Insulin Resistance:
Insulin resistance is a common feature of PCOS. In this condition, the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. To compensate, the pancreas produces more insulin. Elevated insulin levels can stimulate the ovaries to produce excess androgens (male hormones), such as testosterone, which can disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to other PCOS symptoms.
- Hormonal Imbalances:
PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances, including elevated levels of androgens (such as testosterone) and luteinizing hormone (LH) relative to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This imbalance can interfere with normal ovulation, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and other symptoms.
- Inflammation:
Some research suggests that chronic inflammation may contribute to the development of PCOS. Inflammation can impact insulin sensitivity and disrupt ovarian function.
- Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors, such as exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) found in plastics and certain industrial pollutants, may play a role in PCOS development or exacerbation. These chemicals can interfere with hormonal regulation.
❖ Common Symptoms of PCOS
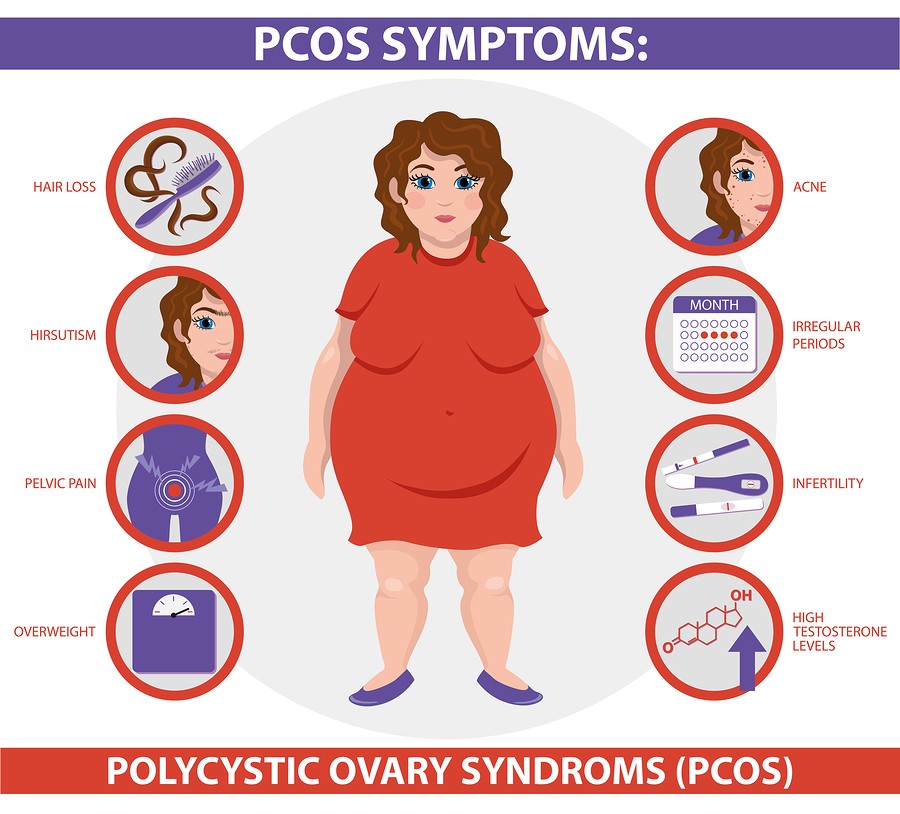
PCOS is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, and the severity and combination of symptoms can vary among individuals. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Menstrual Irregularities:
Irregular periods, including missed periods or infrequent ovulation, are a hallmark of PCOS. Some individuals may also experience heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Menstrual Irregularities in PCOS:
One of the most characteristic and often distressing features of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is menstrual irregularity. Menstrual cycles are a fundamental aspect of a woman’s reproductive health, serving as a key indicator of hormonal balance and overall well-being. In the context of PCOS, menstrual irregularities can manifest in various ways, profoundly affecting a woman’s life, fertility, and self-esteem.
- Understanding Menstrual Irregularities:
In a healthy menstrual cycle, the ovaries release an egg (ovulation), and if fertilization does not occur, the uterine lining is shed, resulting in menstruation. In PCOS, hormonal imbalances disrupt this intricate process, leading to irregular periods and often anovulation, where ovulation does not occur.
- Missed Periods or Amenorrhea:
One of the primary manifestations of menstrual irregularities in PCOS is missed periods or amenorrhea, which refers to the absence of menstrual cycles for an extended duration. Women with PCOS may experience infrequent menstruation, with cycles lasting longer than the typical 28 days or no periods at all. This inconsistency can create uncertainty about fertility and provoke anxiety.
- Oligomenorrhea:
Oligomenorrhea refers to infrequent menstruation characterized by prolonged cycles, typically lasting 35 days or more. Women with PCOS may have oligomenorrhea, which can make it challenging to predict when their next period will occur. This unpredictability can be particularly frustrating for those attempting to conceive.
- Heavy or Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding:
Conversely, some women with PCOS may experience heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding when their periods do occur. This excessive bleeding can lead to discomfort, fatigue, and anemia, further impacting their quality of life.
- Impact on Fertility:
Menstrual irregularities are not only a source of personal distress but also a significant factor contributing to fertility issues in women with PCOS. Anovulation, common in PCOS, reduces the chances of successful conception. Many women with PCOS may struggle to become pregnant and require medical interventions, such as ovulation-inducing medications, to enhance their fertility.
- Psychological and Emotional Impacts:
The emotional toll of menstrual irregularities should not be underestimated. The unpredictability of one’s menstrual cycle can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and uncertainty. Women with PCOS may experience anxiety related to their fertility and hormonal health. The impact on self-esteem can be profound, as the condition may challenge their sense of femininity and body image.
❖ Managing Menstrual Irregularities:
While menstrual irregularities are a hallmark of PCOS, they can be managed and treated to improve overall well-being. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise, can help regulate menstrual cycles. Additionally, healthcare providers may prescribe hormonal contraceptives to regulate periods and manage symptoms.
In situations where fertility is a primary concern, medical interventions such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole may be recommended to stimulate ovulation. Concurrently, embracing lifestyle modifications such as stress reduction and the adoption of a well-balanced diet can play a pivotal role in enhancing hormonal equilibrium and promoting regular menstrual cycles.
- Ovulatory Dysfunction: PCOS frequently leads to anovulation, a condition where the ovaries do not release eggs on a regular basis. This phenomenon can be a contributing factor to infertility.
- Hyperandrogenism: Increased androgen levels can result in physical manifestations such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the face and body), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
- Polycystic Ovaries: On ultrasound imaging, the ovaries of individuals with PCOS may appear enlarged and contain multiple small follicles, giving them a “polycystic” appearance.
- Insulin Resistance: Many individuals with PCOS experience insulin resistance, which can lead to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Skin Issues: Common skin problems in individuals with PCOS include acne, oily skin, and darkening of the skin in specific areas known as acanthosis nigricans.
- Emotional and Mental Health Challenges: PCOS can also impact emotional and mental well-being. It’s frequently associated with symptoms of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
❖ Empowering Women with PCOS:
- Knowledge is Power: Understanding the causes and symptoms of PCOS is the first step toward empowerment. Knowledge enables women to advocate for their health, make informed decisions, and work collaboratively with healthcare providers.
- Seeking Medical Guidance: If you suspect you have PCOS or have already received a diagnosis, seeking medical guidance is crucial. Healthcare professionals can help you navigate the complexities of the condition, offering personalized treatment plans and monitoring to manage symptoms and promote fertility.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle plays a pivotal role in managing PCOS. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help regulate menstrual cycles and improve hormonal balance. Stress reduction techniques can also have a positive impact on overall well-being.
- Support Networks: Connecting with support networks, both online and offline, can provide invaluable emotional support. Sharing experiences and strategies with others who understand the challenges of PCOS can be comforting and empowering.
- Fertility Options: For those seeking to conceive, various fertility treatments and medications are available to induce ovulation and increase the chances of pregnancy. Consulting a fertility specialist can provide guidance on the best course of action.
- Self-Care: Prioritizing self-care is essential. Managing stress, practising self-compassion, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can contribute to improved emotional well-being.
❖ Conclusion: Empowering Women with PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects countless women worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the causes, symptoms, and challenges associated with PCOS, with a particular focus on the significant impact of menstrual irregularities.
PCOS is more than just a medical diagnosis; it’s a condition that can deeply influence a woman’s physical and emotional well-being. The irregular menstrual cycles, missed periods, and anovulation associated with PCOS can bring about a range of challenges, from fertility concerns to emotional distress.
However, it’s important to emphasize that PCOS is a manageable condition, and with the right knowledge, support, and proactive steps, women with PCOS can take control of their health and lead fulfilling lives.
In conclusion, while PCOS presents unique challenges, it is a condition that can be managed effectively. Empowering women with PCOS involves not only addressing the physical aspects of the condition but also attending to the emotional and psychological aspects. With the right resources, support, and a proactive approach to health, women with PCOS can embrace their journey to wellness, fertility, and self-discovery. By sharing knowledge and fostering a sense of empowerment, we can help women with PCOS lead healthier, happier lives and overcome the challenges posed by this complex condition.