❖ Introduction:
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, social media has emerged as a powerful tool that transcends personal connections and entertainment. Its potential extends to the field of pharmacy, where it plays a significant role in both practice and education. This blog post explores how social media is transforming pharmacy practice and education, highlighting its advantages, challenges, and future prospects. In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the influence of social media extends far beyond the realm of personal connections and entertainment. It has emerged as a dynamic force shaping various professional sectors, including the field of pharmacy. Social media’s unique ability to connect, inform, and engage has led to its seamless integration into both pharmacy practice and education, revolutionizing the way pharmacists interact with patients, collaborate with colleagues, and disseminate crucial healthcare information.
As a bridge between individuals and information, social media has found a significant place in pharmacy practice, enabling pharmacists to reach a broader audience with accurate and relevant health-related content. It serves as a potent platform to educate patients about medications, possible side effects, and ways to enhance their overall well-being. Through succinct and visually engaging posts, pharmacists can simplify complex medical jargon, empowering patients to make informed decisions about their health management.
Moreover, the intersection of social media and pharmacy practice is not limited to patient education alone. It serves as an essential conduit for pharmacists to extend their impact beyond the confines of the pharmacy walls. From raising awareness about medication recalls to advocating for public health campaigns, pharmacists harness the real-time nature of social media to contribute to community health on a larger scale. In the sphere of pharmacy education, social media’s influence is equally transformational. Traditional pedagogical methods are now augmented by the interactivity and immediacy that social media platforms offer. Pharmacy students and educators can engage in real-time discussions, share resources, and collaborate on projects in virtual learning communities. This collaborative and multi-directional exchange of knowledge helps bridge the gap between theoretical concepts taught in classrooms and their practical applications in real-world scenarios.
The potential of social media for education goes beyond classroom confines. Guest lectures and live sessions by practising pharmacists and industry experts can provide students with insights into the diverse facets of the pharmacy profession. By virtually connecting students with professionals from various domains, social media nurtures a broader perspective and enriches the learning experience. However, the integration of social media into pharmacy practice and education is not without its challenges. Ensuring patient privacy and confidentiality while responding to health queries on public platforms demands a delicate balance between providing informative content and safeguarding sensitive information. Furthermore, the open nature of social media leaves room for the inadvertent spread of misinformation, emphasizing the importance of verifying and sharing only evidence-based content.
Navigating ethical considerations is paramount when pharmacists engage on social media platforms. Striking a balance between personal expression and professional representation requires a mindful approach, as social media activity reflects the pharmacist’s identity and values. Adhering to ethical guidelines and maintaining a high standard of professionalism is essential to uphold the reputation of the pharmacy profession in the digital age. As social media continues to evolve, the future prospects for its role in pharmacy practice and education are promising. The seamless integration of tele-health services within social media platforms could enable pharmacists to provide virtual consultations and offer timely advice to patients, bridging the geographical gap between healthcare providers and individuals seeking guidance. Additionally, social media could emerge as a hub for continuing education, curating a wealth of pharmacy-related content, webinars, and discussions, thereby fostering a culture of continuous learning among pharmacy professionals.
❖ The Intersection of Social Media and Pharmacy Practice:

Social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn, have revolutionized how pharmacists engage with patients, healthcare professionals, and the public like:-
- Patient Education and Empowerment: Social media provides pharmacists with a direct channel to educate patients about medication usage, side effects, and potential interactions. Timely posts can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health.
- Medication Safety Awareness: Pharmacies can use social media to disseminate information about medication recalls, safety alerts, and emerging health concerns. Such posts contribute to enhancing public safety and awareness.
- Community Engagement: Social media facilitates engagement with local communities. Pharmacies can use platforms to promote health campaigns, vaccination drives, and wellness events, fostering a sense of community involvement.
❖ Social Media’s Role in Pharmacy Education:
In the realm of pharmacy education, social media’s impact is equally profound. It offers new avenues for interaction, collaboration, and knowledge sharing among students and educators such as:
- Virtual Learning Communities: Social media platforms enable the creation of virtual communities where pharmacy students and educators can exchange ideas, share resources, and discuss complex topics beyond the classroom.
- Real-World Case Studies: Pharmacy educators can utilize social media to present real-world case studies, encouraging students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
- Guest Lectures and Insights: Inviting guest pharmacists, researchers, or industry experts for live sessions on social media platforms exposes students to diverse perspectives and the latest trends in pharmacy.
❖ Advantages of Social Media in Pharmacy:
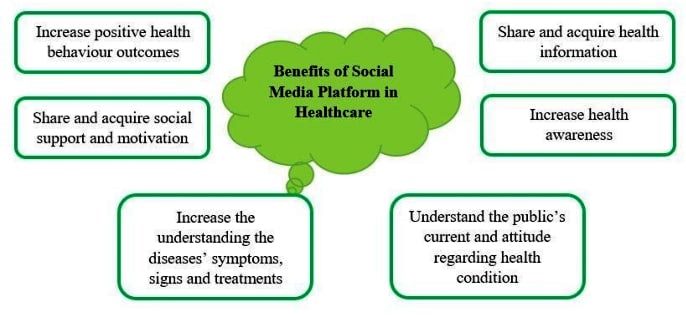
- Rapid Dissemination of Information: Social media allows pharmacies to quickly share information, news, and updates, ensuring that patients and the public stay well-informed.
- Improved Patient-Pharmacist Communication: Direct messaging and commenting features on social media platforms enable patients to ask questions and receive personalized responses from pharmacists.
- Networking and Collaboration: Pharmacists can connect with peers, other healthcare professionals, and experts globally, fostering collaboration and professional growth.
- Engagement and Behaviour Change: Engaging content on social media can motivate patients to adopt healthier habits, adhere to medication regimens, and prioritize their well-being.
❖ Challenges and Considerations:
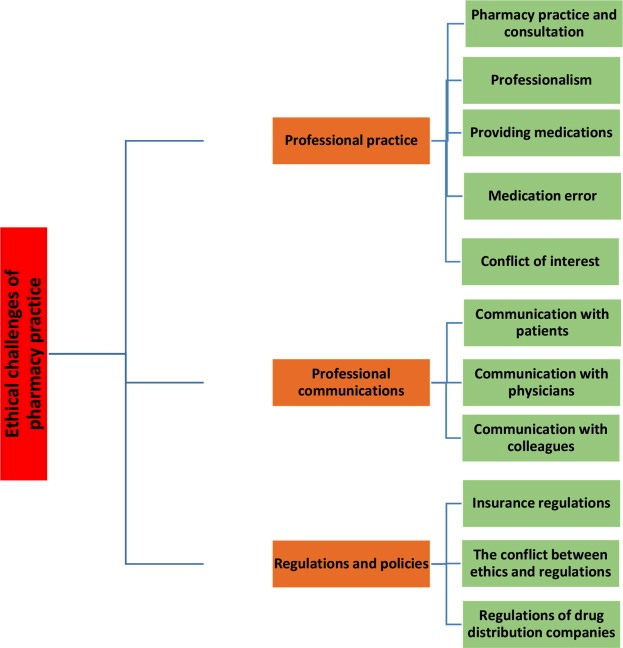
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Maintaining patient confidentiality and privacy while addressing health queries or concerns on public platforms is a challenge that requires careful handling.
- Misinformation and Dissemination of Inaccurate Information: The open nature of social media can lead to the spread of misinformation. Pharmacists must ensure that the information they share is accurate and evidence-based.
- Ethical Guidelines: Pharmacists need to navigate professional codes of conduct and ethical guidelines while engaging on social media, ensuring that their online presence reflects their professional identity.
Future Prospects and Recommendations:
- Integration of Tele–health: Social media can complement the growing trend of tele-health services, enabling pharmacists to provide virtual consultations and advice to patients.
- Continuing Education Platforms: Social media could evolve into a hub for continuous learning, with curated content, webinars, and discussions for pharmacy professionals seeking to expand their knowledge.
- Advocacy and Policy Influence: Pharmacist engagement on social media can raise awareness about policy issues and advocate for changes that positively impact patient care and the profession.
❖ Conclusion:
Social media’s integration into pharmacy practice and education has opened new doors for communication, collaboration, and patient care. While challenges exist, the benefits far outweigh them. Pharmacists who navigate the social media landscape thoughtfully can enhance patient outcomes, contribute to professional growth, and advance the field of pharmacy into a digitally connected future. infiltrating various aspects of pharmacy practice and education. Its capacity to engage, educate , and advocate positions it as an invaluable asset in the pharmacist’s tool-kit. However, embracing this digital transformation requires a mindful approach that considers the ethical, privacy, and accuracy challenges, ensuring that the positive impact of social media on pharmacy is harnessed responsibly and effectively.