❖ Introduction:
The ‘Crew Dragon’ capsule made its flawless debut on May 30th, 2020, as the world watched, intended for transporting astronauts to and from the International Space Station. The joint effort between NASA and SpaceX marked a groundbreaking achievement in mechanical and aerospace engineering, highlighting cutting-edge technology. The spacecraft not only had a remarkable design but also incorporated a range of contemporary elements, resembling those found in science fiction spacecraft. These innovations encompassed items such as 3D-printed helmets, the 3D-printed Super Draco Engine, touch screen displays, and an automated docking system. These advancements are anticipated to serve as a source of inspiration and empowerment for future generations over an extended period.
Stepping back for a wider view, let’s reflect on the fundamental domain of engineering, which stands as the oldest and most all-encompassing discipline. This field harmoniously merges mathematical principles, engineering physics, and materials science to conceptualize, assess, construct, and proficiently oversee the functionality of technological prototypes.
❖ What is Mechanical Engineering?
Mechanical engineering necessitates a grasp of fundamental principles from various disciplines such as Chemistry, Physics, Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Aerospace Engineering, and Automobile Engineering. This knowledge is essential for the design, creation, and operation of machinery. Mechanical engineering revolves around core principles encompassing mechanics, dynamics, material science, strength analysis, thermodynamics, structural assessment, and electrical energy. This field also incorporates tools like Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM). Its applications are extensive, ranging from scrutinizing vehicle design and performance to spanning across various sectors such as aircraft, ships, robotics, nuclear power plants, transportation, and more. Additionally, mechanical engineers are increasingly delving into areas like composites, nanotechnology, and particularly, the field of Mechatronics.
According to the latest NASSCOM EY report, the rise of Artificial Intelligence is anticipated to lead to the replacement of several job positions. This transformation could see roles like Design Engineer shifting towards Interaction Designers, Operation Excellence Managers transitioning into Continuous Improvement Managers, Mechanical positions evolving into Mechatronics Control Engineers, Clay Modelers transforming into 3D Clay Modelers, and Customer Care Executives potentially becoming Customer Care Experts. Consequently, it’s clear that there’s a necessity for us to upgrade and adapt our skill sets accordingly.
❖ Why is Mechanical Engineering the foundational pillar of all engineering disciplines?
Mechanical engineering is often called the “ foundational pillar of all engineering disciplines ” due to its foundational principles that form the basis for many other engineering disciplines. Its broad scope and fundamental concepts are widely applicable across various fields, making it a cornerstone of engineering knowledge.
As passed down through generations, Mechanical engineering stands as an enduring and essential field. Its perpetual relevance is rooted in being the foundation for various other engineering disciplines, as mentioned below. Practically every industry, whether it’s medicine, automotive, construction, electrical, or IT, incorporates some form of mechanical applications.
Branches of Mechanical Engineering:
As mechanical engineering serves as the foundation for various engineering disciplines, there exist numerous areas of expertise within its scope. Here are the most prevalent branches where graduates can pursue their careers.
1. Acoustical Engineering
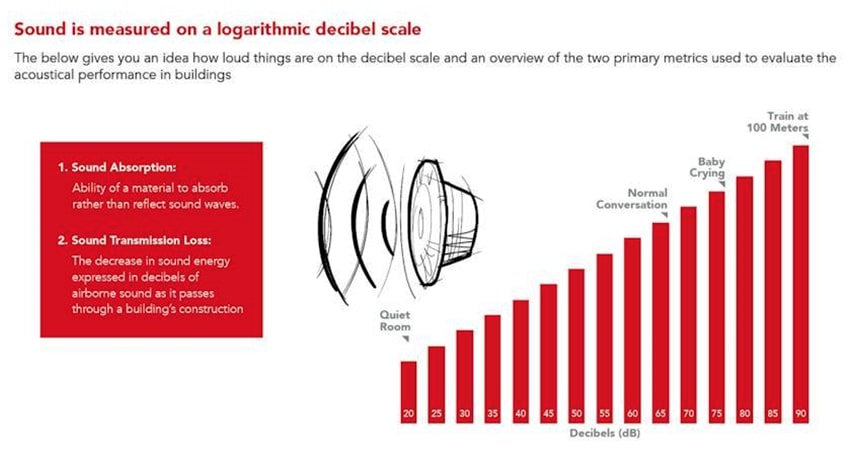
Commencing in the late 1920s, this field focuses on examining sounds, vibrations, and frequencies inherent in every substance. Acoustical engineers play a pivotal role in mitigating noise pollution, recognizing its detrimental effects on both animals and humans. Their work extends beyond noise reduction, encompassing diverse domains like medical applications for ultrasound technology and the creation of high-quality concert halls, cinemas, and precise ultrasonic scans.
Embedded across various facets of contemporary society, from crafting automobile structures to aerospace engineering, this discipline is prominently employed for managing and regulating both sound and vibrations.
2. Aerospace Engineering
It involves a blend of engineering disciplines and technology, encompassing areas like aerodynamics, propulsion, materials science, avionics (handling the electronic aspect of aerospace engineering), structural analysis, design, and production. This domain primarily focuses on creating and advancing aircraft and spacecraft. It branches into two closely connected fields: Aeronautical and Astronautical Engineering. Its applications span across military use and space exploration.
3. Automotive Engineering

This field revolves around designing and developing various road vehicles, involving modifications and dynamics. It utilizes tools like SolidWorks and ANSYS for vehicle design, integrates multiple disciplines including electronics and software, and heavily relies on research and the application of mathematics and physics. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) stands as a key source in this realm, addressing functions related to production, development, and manufacturing.
4. Marine Engineering
Certainly! Archimedes and Thomas Newcomen were influential figures in marine engineering. Archimedes contributed innovations in ancient times, while Thomas Newcomen’s steam engine revolutionized mining. Marine engineering involves the design, upkeep, and enhancement of sea-going vessels, along with studying oceanic elements and creating structures like offshore wind farms and oil platforms. The Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers (SNAME) serves as a valuable resource in this field.
5. Mechatronics Engineering
Initially, Mechatronics Engineering combined Mechanical and Electronics disciplines. However, as this field progressed, its definition expanded to encompass a wider array of technical domains including robotics, telecommunications, coding, and more. The term “Mechatronics” was coined by Tetsuro Mori, a Japanese engineer, in 1969. Industrial robots stand out as a prime example within this field.
6. Railway Engineering

It began with the emergence of railways in the early 19th century, amid the Industrial Revolution, leading to the necessity for a specialized group of engineers capable of overseeing the design, development, and all aspects related to Railway Engineering. This field involves the design, construction, and maintenance of tracks to ensure safe and efficient rail operations.
❖ Numerous avenues exist for study and exploration within the realm of Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical Engineers possess a wide array of job opportunities across various industrial sectors. It stands as one of the most widely applied engineering disciplines, spanning from medical devices to rocket technology. For students in the early stages of college, it is crucial to identify personal strengths before selecting a specific area within this field, as it demands considerable research and exploration. Hence, it is highly important from where an individual is studying about the core knowledge of Mechanical Engineering!
Here comes the name of IIMT University. IIMTU stands out as the premier destination for learning mechanical engineering, offering a comprehensive and cutting-edge academic experience. The faculty members comprise accomplished professionals and scholars, ensuring high-quality education. State-of-the-art laboratories and workshops provide hands-on learning opportunities, fostering practical skills. The curriculum is designed to align with industry demands, equipping students with relevant knowledge and expertise. Regular industry interactions, workshops, and internships further enhance real-world exposure. The university emphasizes research, encouraging students to explore innovative solutions for contemporary engineering challenges. With a commitment to holistic development, IIMT University emerges as the best choice for aspiring mechanical engineers, shaping future industry leaders; consistently recognized as the best placement university in North India. Let’s see an overview of what areas of education covered at IIMT University:
1. Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is the study of how gases influence the motion of objects. Its primary focus lies in understanding the forces of drag and lift, predominantly generated by air movement over and around solid bodies. Engineers apply aerodynamic principles in various fields, such as vehicle and aircraft design. This discipline is a subset of fluid dynamics.
2. Fluid mechanics
A subset of continuum mechanics, fluid mechanics is a physics branch that delves into the behavior of continuous materials, particularly fluids (liquids, gases) when under external forces causing deformation. Fluid mechanics divides into two categories: fluid statics, studying fluids at rest, and fluid dynamics, examining fluids in motion. It primarily involves a mathematical approach, often addressed through numerical methods on computers, like Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). This discipline finds applications across various fields including Aerospace, Biomechanics, Metrology, Automotive, and numerous others.
3. Combustion, Energy and Environment
Mechanical engineers specialize in designing combustion-related systems like internal combustion engines and gas turbines, aiming to enhance efficiency and minimize pollution. Ongoing university research explores alternative liquid fuels for aircraft and automobiles, super-adiabatic combustion, and solid particle combustion with water for hydrogen production.
5. Mechanical design
Mechanical design translates ideas into reality by collecting requirements, conceptualizing, and creating comprehensive designs. It involves designing parts, components, and various mechanical systems like shafts, gears, bearings, and fasteners. Considerations include weight, size, manufacturability, safety, and reliability. A successful mechanical design requires clear statements detailing functions, specifications, and evaluation criteria. Tools like AutoCAD, SOLIDWORKS, CATIA, Inventor, and Fusion 360 are commonly used for product design.
6. Manufacturing
It is a vast and ever-evolving field, adapting alongside the continuous advancements. The process of converting raw materials into valuable products involves multiple steps. Beginning with product design and specifications, it progresses towards creating a market-ready product. Among the key responsibilities of a mechanical engineer is to explore diverse production methods and techniques. Manufacturing encompasses various methods including Mass manufacturing, Lean manufacturing, Rapid manufacturing, Just-in-time manufacturing, Agile manufacturing, Flexible manufacturing, and several others.
7. Material science
Material science explores how materials’ structures affect their properties, crucial in product design. Material selection depends on performance and can be customized for specific needs. Understanding processing-structure-properties is the material paradigm, applied in nanotechnology, biomaterials, and metallurgy.
6. Dynamics
This branch of mechanics, focuses on forces and their impact on the movement of solid objects. Understanding the fundamentals of vehicle dynamics is essential for analyzing vehicle performance and efficiency. It encompasses topics including braking systems, suspension, steering mechanisms, tires, wheels, and transmission systems such as gearbox, engine, and axles.
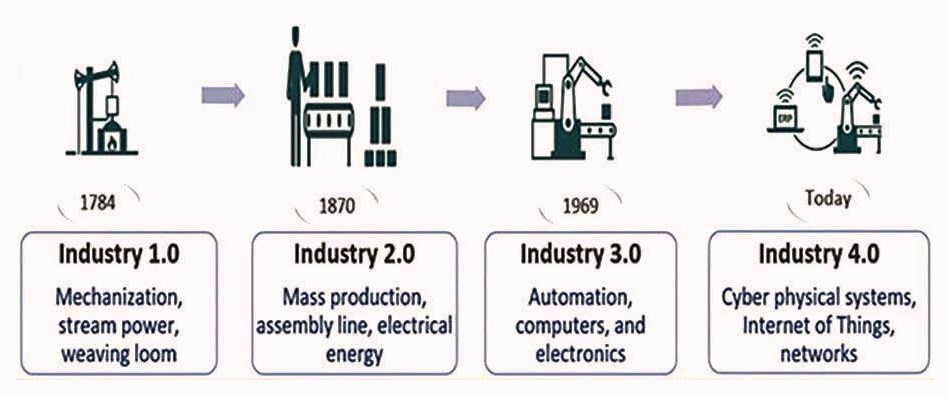
❖ Industry 4.0 and its Impact
Industry 4.0 represents the merging of technologies, erasing the boundaries between the physical, digital, and biological realms. This phase introduces a highly sophisticated era where machines are not just smart but remarkably advanced. Technologies like the Internet of Things, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, and Additive Manufacturing (AM) are revolutionizing mechanical engineering design and production within Industry 4.0 This revolution is fundamentally changing how we design and manufacture products, leading to significantly more reliable outcomes compared to traditional methods.
With the onset of Industry 4.0, engineers will adopt digital tools and technologies, enabling the efficient production of top-quality goods. Utilizing data-driven intelligence, they’ll swiftly respond to consumer demands, fostering a rise in customized products tailored to individual preferences. This trend is poised to enhance customer loyalty. Moreover, machines like engines, turbines, locomotives, and numerous medical devices are evolving to become analytical and predictive. They’ll intelligently and autonomously communicate with each other and us. This predictive capability aids in foreseeing potential breakdowns, reducing unforeseen errors and faults, thereby boosting overall productivity.
Mechanical engineering roles are influenced by multiple factors and parameters. Over the next five years, inevitable forces such as Globalization, Demographic shifts, and the integration of Industry 4.0 will demand that mechanical engineers enhance and update their skill sets.
By 2022, around 5% to 10% of workers in automotive and mechanical sectors could hold new job roles. An estimated 50% to 55% of the workforce might require significantly changed skill sets. Additionally, 10% to 15% of employees face potential job threats within these industries.
The prevalence of data storage and analysis has resulted in a significant transformation, fostering the creation of various job roles across nearly all sectors, such as automotive analytics engineer, research analyst, quality analyst, and more.
❖ Counclusion
Mechanical Engineering, the cornerstone of diverse engineering fields, is advancing with technology, Industry 4.0 integration, and data analytics. It encompasses various sectors like aerospace, automotive, and marine engineering. This discipline incorporates Acoustical, Aerospace, Automotive, Marine, Mechatronics, and Railway Engineering, and branches into areas like Aerodynamics, Fluid Mechanics, Combustion & Energy, Mechanical Design, Manufacturing, Material Science, and Dynamics. The industry’s evolution requires engineers to adapt to digital tools and updated skill sets to meet future demands.
Looking for an engineering university that stands out in Uttar Pradesh? Look no further than IIMT University in Meerut. Renowned as one of the top private universities in UP, IIMTU has earned its reputation for excellence in engineering education. What sets this institution apart is not just its academic rigor but also its commitment to ensuring exceptional placements for its graduates. IIMT University equips its students with the knowledge, skills, and practical experience needed to thrive in the competitive job market. With state-of-the-art facilities, experienced faculty, and a strong industry interface, IIMT University paves the way for a promising career in engineering. Choosing IIMT University means investing in a quality education that opens doors to a world of opportunities.
Author: Mr. Ajay Pratap
HoD Mechanical Engineering, IIMTU
For more information on our comprehensive education- 🌐 click here