❖ Introduction:
Pharmacy is a diploma course in the Pharmacy in this student study a many subjects like H.A.P Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Pharmaceutics, Community Pharmacy and Pharmacology etc. In Pharmacology subject, student study various type of diseases & symptoms. Diabetes is one of them, in today’s time approx 10 lacks people are affected by this disease, In this blog we will see the diabetes type and what is diabetes complication. Hopefully this blog is very useful for those people and student to know about the diabetes disease.
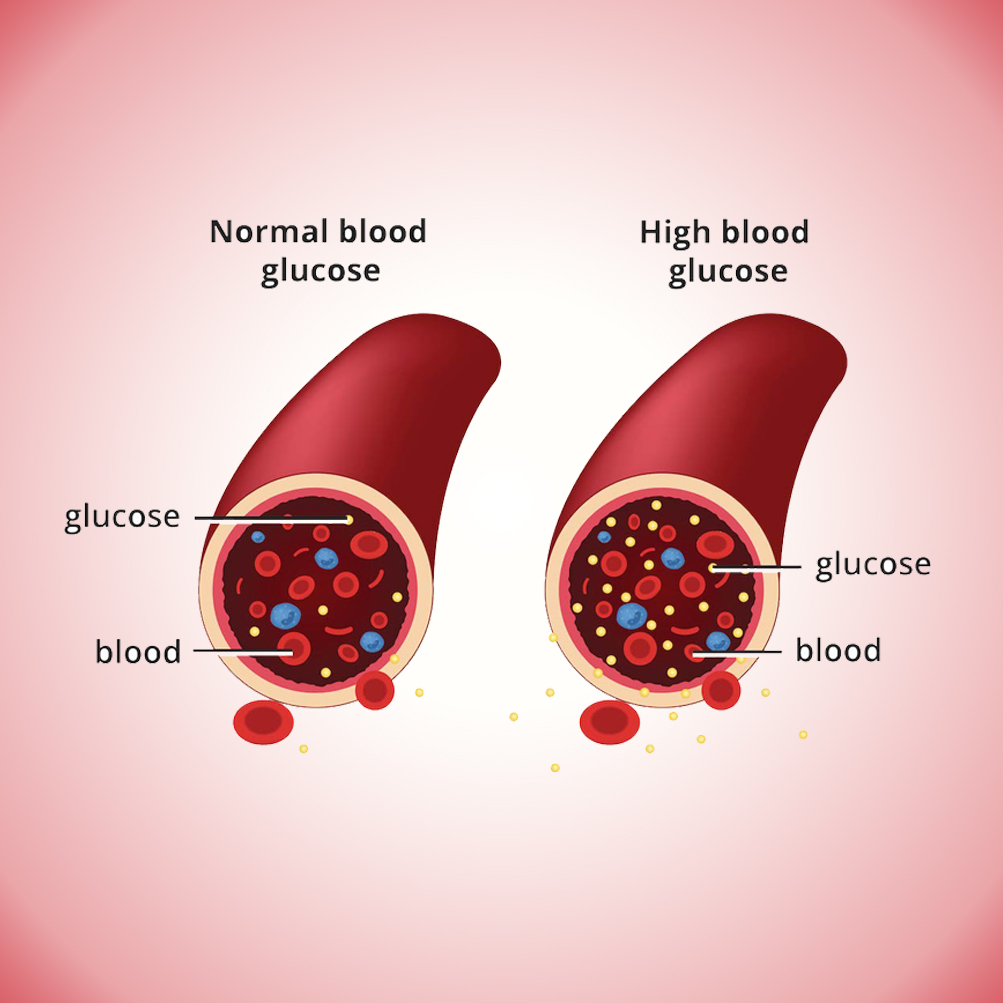
The diabetes is a endocrine metabolic disorder, characterised by elevated blood sugar level. Hyperglycaemia arises due to either absolute or relative insulin deficiency or cellular resistance towards insulin.
Diabetes is a long-term medical illness that interferes with your body’s ability to control blood sugar or glucose. The hormone insulin, which the pancreas produces, aids in regulating the intake and utilisation of glucose, which is an essential source of energy for the body’s cells.
There are various forms of diabetes, such as:
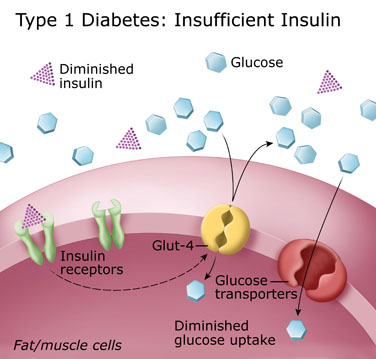
1. Kind 1 Diabetes:
When the pancreas is unable to create enough insulin, this kind of diabetes develops. Despite the fact that it can manifest at any age, it is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescent. For the rest of their lives, type 1 diabetics must take insulin therapy to control their blood sugar levels.
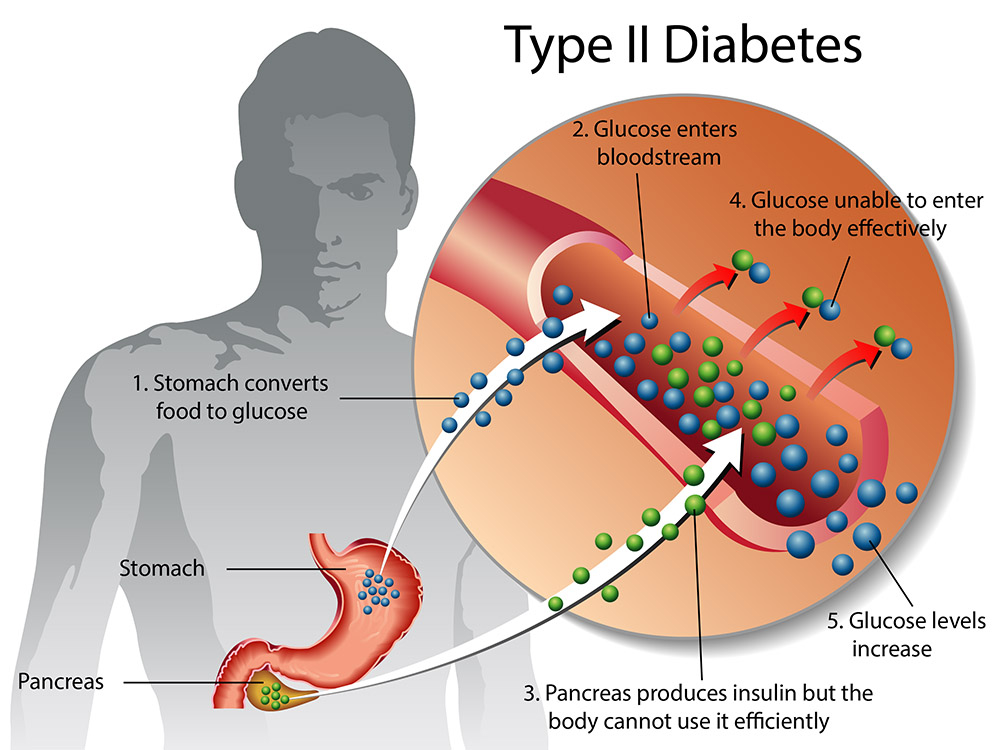
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
The most prevalent kind of diabetes, type 2, usually manifests in maturity, while paediatric and adolescent diagnoses are on the rise. In order to maintain normal blood sugar levels, the body either stops producing enough insulin or develops an insulin resistance. The onset of type 2 diabetes can be influenced by lifestyle choices such as poor food, inactivity, weight, and heredity. A nutritious diet, moderate exercise, and, occasionally, oral medicines or insulin are all part of the treatment process.
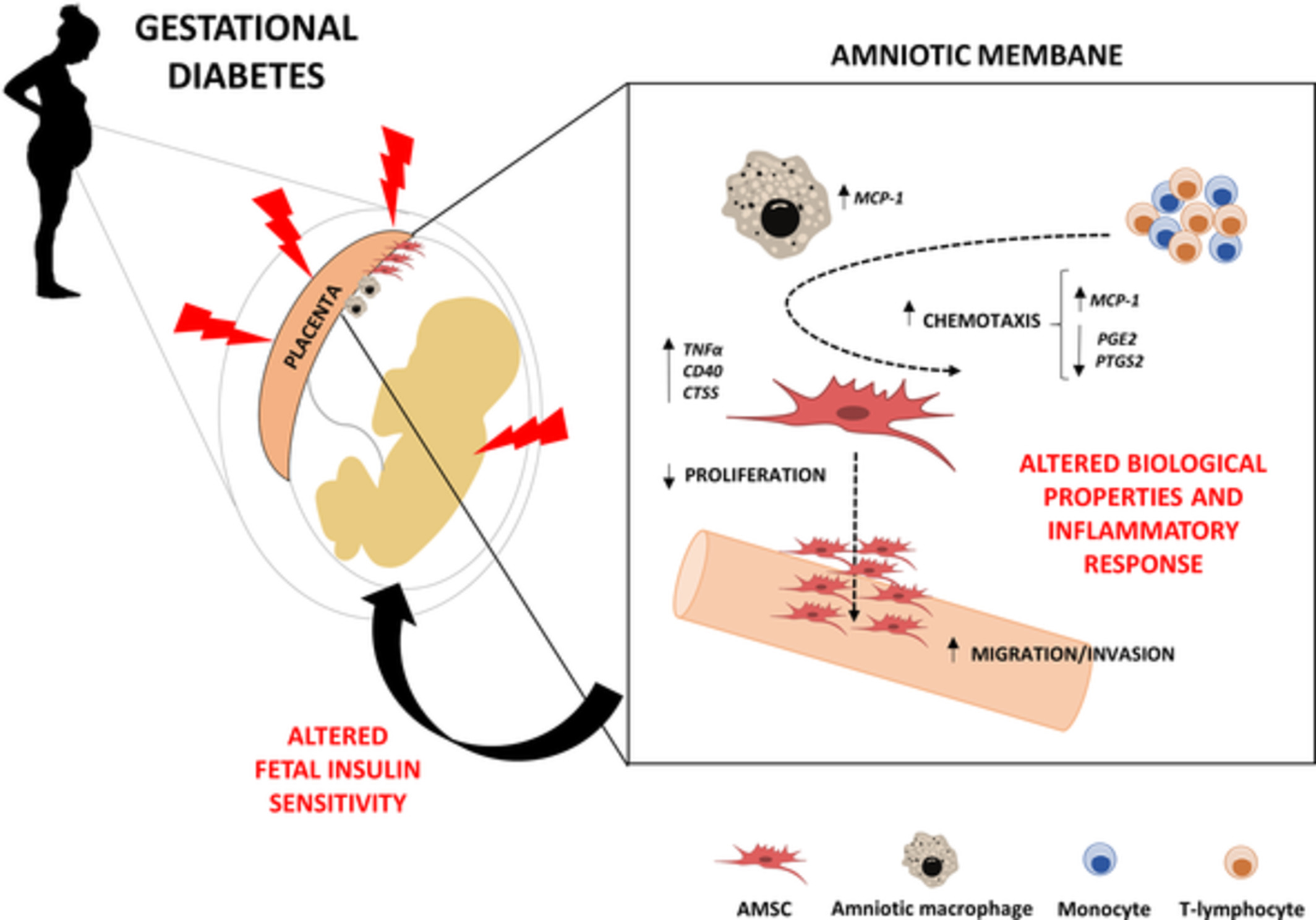
3. Gestational Diabetes:
Some women who have never had diabetes before are affected by this type of pregnancy-related diabetes. After childbirth, it normally goes away, but it raises the possibility of type 2 diabetes later in life. Increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, weariness, hazy eyesight, sluggish wound healing, and recurrent infections are all signs of diabetes. However, some persons with type 2 diabetes may not immediately show any obvious symptoms. The goal of managing diabetes is to keep blood sugar levels within a specific range using a variety of strategies, such as:
- Drugs: To help control blood sugar levels, patients with diabetes may need to take insulin injections, oral medicines, or other injectable drugs.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels with a glucose meter enables people to make well-informed choices regarding their diet, exercise routine, & medicine.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, & maintaining a healthy weight are essential for managing diabetes.
- Education and Support: Diabetes self-management education and support programs can provide individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to manage their condition effectively.
- Herbal Medicine:
Herbal medicine has been used for centuries in various cultures as a complementary or alternative approach to managing certain health conditions, including diabetes. It’s important to note that while some herbs may show promise in managing blood sugar levels, they should not replace conventional medical treatment or prescribed medications. If you have diabetes, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before incorporating any herbal remedies into your diabetes management plan. They can provide guidance on potential interactions, proper dosages, and monitor your progress.
Here are a few herbs that have been studied for their potential effects on diabetes:
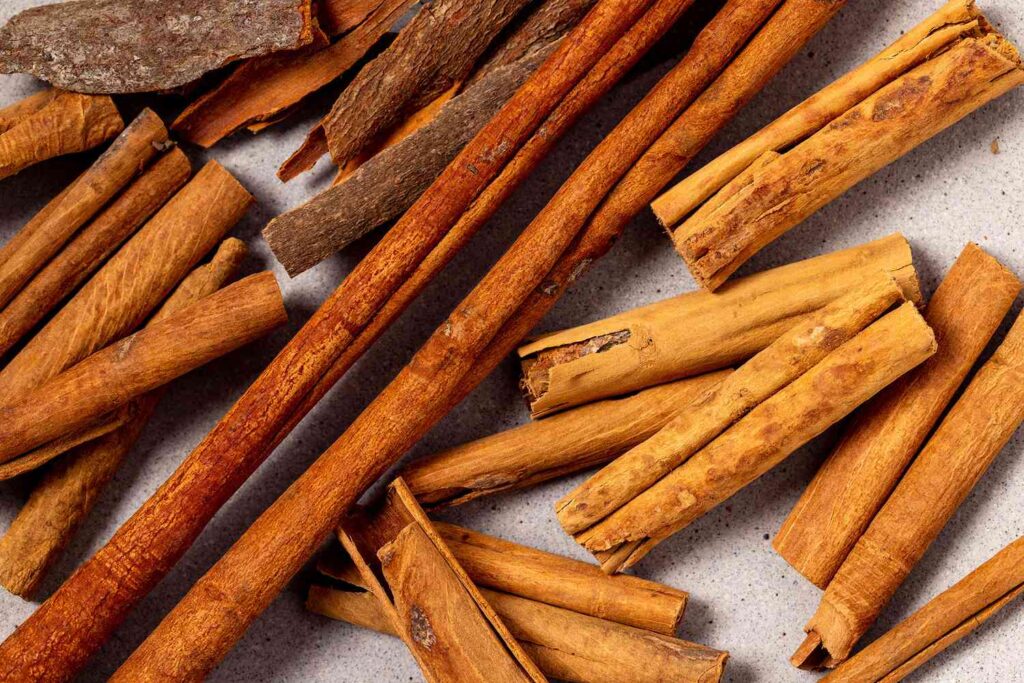
1.Cinnamon: Some studies have suggested that cinnamon may help improve blood sugar control by increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness and determine the appropriate dosage.

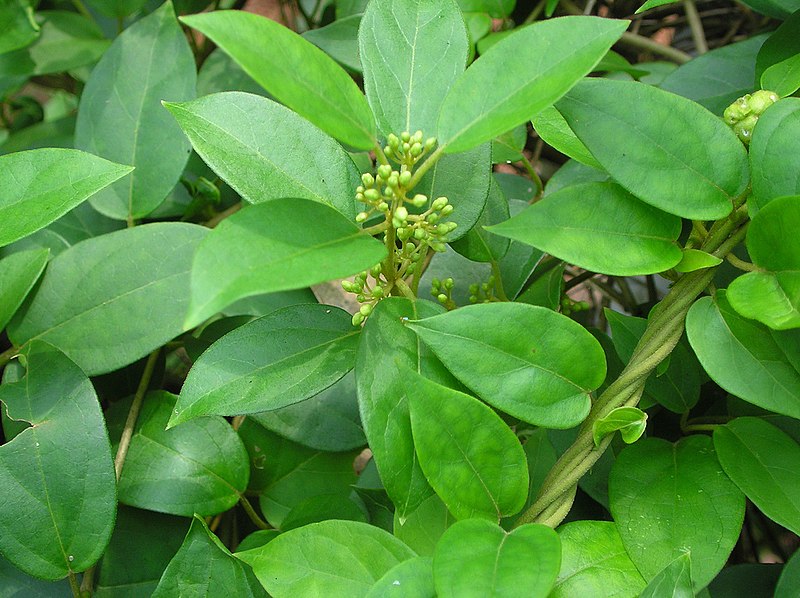
2.Gymnema Sylvestre: Gymnema Sylvestre is an herb commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine. It has been traditionally used to help regulate blood sugar levels. Some studies have shown that it may reduce sugar cravings and help lower blood sugar levels, but further research is needed.

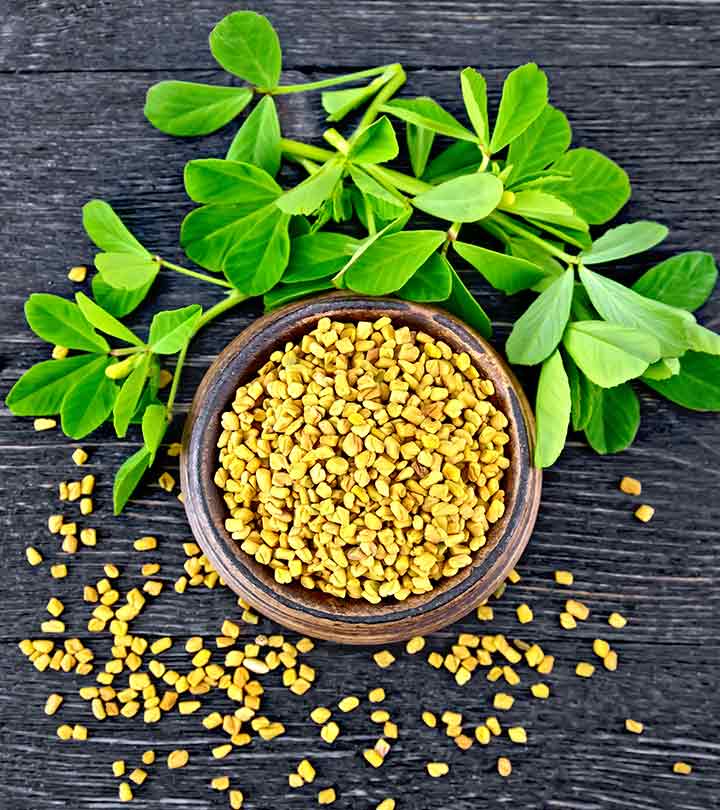
3.Fenugreek: Fenugreek seeds have been found to have anti-diabetic properties. They may help lower blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose and improving insulin sensitivity. However, more research is necessary to establish its efficacy and safety.

4.Bitter Melon: Bitter melon, also known as bitter gourd or Momordica charantia, is a fruit commonly consumed in Asian countries. It contains compounds that may have blood sugar-lowering effects. Some studies have shown potential benefits in reducing blood sugar levels, but more research is needed to determine its optimal use.

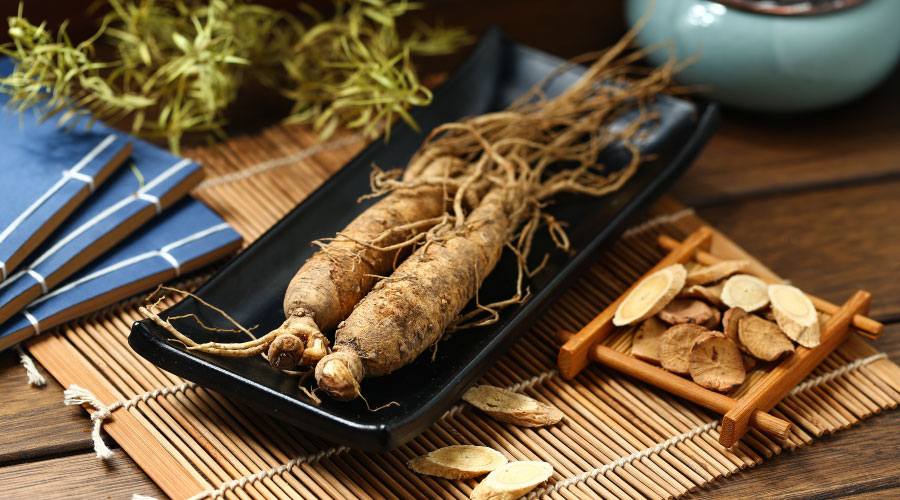
5.Ginseng: Certain types of ginseng, such as American ginseng and Korean red ginseng, have been studied for their potential anti-diabetic properties. They may help improve glucose metabolism and enhance insulin sensitivity. However, their effects can vary, and it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using ginseng as it may interact with certain medications.

❖ Importance of Herbal Medicine:
Herbal medicines have been used for centuries and continues to be an important part of healthcare in many cultures. Here are some reasons why herbal medicine holds importance:
- Historical Significance: Herbal medicine has a rich history and has been used for generations in different cultures worldwide. Traditional systems of medicine, such as Ayurveda, (TCM) & Native American medicine, have relied heavily on herbal remedies to treat various ailments.
- Natural Approach: Herbal medicine utilizes plant-based remedies, which are considered natural & often well-tolerated by the body. Many people prefer herbal medicine as a more holistic approach to healthcare, aiming to support the body’s natural healing processes.
- Accessibility: Herbal remedies are often readily available, affordable, and can be prepared at home or obtained from local markets. This accessibility makes herbal medicine an attractive option, especially for individuals with limited access to conventional healthcare.
- Potential Health Benefits: Certain herbs have been scientifically studied and shown to possess medicinal properties. They may have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and other beneficial effects on the body. Some herbs have been found to support specific bodily functions or target certain health conditions.
- Complementary Approach: Herbal medicine is often used as a complementary or alternative therapy alongside conventional medical treatments. It can provide additional support for overall health and well-being and may help manage certain symptoms or side effects associated with conventional treatments.
- Personalisation: Herbal medicine allows for personalized approaches to healthcare. Herbalists or practitioners of traditional medicine often consider an individual’s unique constitution, symptoms, and overall health to prescribe specific herbs or herbal formulations that are tailored to the person’s needs.
- Cultural Heritage: Herbal medicine carries cultural significance and knowledge passed down through generations. It plays an essential role in preserving cultural traditions, wisdom, and healing practices.
❖ Formulation of Herbal Products:
The formulation of herbal products involves the preparation and combination of various herbs and other natural ingredients to create remedies or products with specific therapeutic purposes. Here are the key steps involved in the formulation process:
- Selection of Herbs: The first step is to identify and select the appropriate herbs for the desired product. This selection is based on the herbs’ medicinal properties, compatibility with other ingredients, and their traditional use or scientific evidence supporting their efficacy.
- Extraction Methods: Once the herbs are chosen, the next step is to extract the active compounds from the plant material. Common extraction methods include maceration (soaking herbs in a solvent), decoction (boiling herbs), infusion (steeping herbs in hot water), or using specialized techniques like distillation or supercritical fluid extraction. The choice of extraction method depends on the properties of the herbs and the desired components to be extracted.
- Standardisation: Standardisation involves ensuring the consistency and quality of the herbal product. It includes identifying and quantifying specific bio-active compounds or marker compounds within the herbal extract. Standardization helps in determining the potency and therapeutic efficacy of the product and ensures batch-to-batch consistency.
- Formulation Development: In this step, the herbal extracts or ingredients are combined in specific proportions to create the desired formulation. Other natural ingredients like oils, waxes, emulsifiers, preservatives, or flavouring agents may also be added to enhance the product’s stability, texture, aroma, or taste.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process involves preparing the herbal formulation in large quantities. This may include mixing the ingredients, heating or cooling, homogenization, filtration, and filling into suitable containers or packaging. Good manufacturing practices (GMP) and quality control measures are followed to ensure product safety, efficacy, and consistency.
- Dosage Forms: Herbal products can be formulated into various dosage forms depending on the intended use and target audience. Common dosage forms include tablets, capsules, liquids (syrups, tinctures, extracts), creams, ointments, gels, powders, or teas. The choice of dosage form depends on factors like stability, bio availability, convenience of administration, and patient preference.
- Quality Assurance and Testing: Herbal products undergo rigorous quality control testing to ensure their safety, efficacy, and adherence to regulatory standards. This may include testing for contaminants, potency, purity, stability, and other quality parameters. Quality assurance procedures help identify any potential issues and ensure that the products meet the required specifications.