❖ Introduction
Migraine is a complex neurological condition characterized by recurrent headaches that can cause significant pain and other associated symptoms. It is important to understand the classification and types of migraines as it can help individuals and healthcare professionals in accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and effective management strategies. In this article, we will delve into the classification system and explore the different types of migraines.
➢ Migraine Classification:
Migraines are classified based on the presence or absence of an aura, a sensory or visual disturbance that often precedes the headache phase. The International Headache Society (IHS) has established a classification system known as the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD). According to the ICHD-3 criteria, migraines can be categorized into two primary types:
1.Migraine without Aura (Common Migraine):
-
- Accounts for the majority of migraines.
- Headache occurs without the presence of an aura.
- May include symptoms such as moderate-to-severe pain, throbbing sensation, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound.
2. Migraine with Aura (Classic Migraine):
-
- Involves a neurological symptom or aura preceding the headache phase.
- Auras are usually visual disturbances, such as flashing lights or blind spots.
- Aura symptoms typically last for about 20 minutes to an hour and are followed by the headache phase.
➢ Types of Migraines
1. Hemiplegic Migraine:
-
- Characterized by temporary paralysis or weakness on one side of the body (hemiplegia) during or after the aura phase.
- Additional symptoms may include visual disturbances, difficulty speaking, and sensory abnormalities.
- Aura symptoms typically last for about 20 minutes to an hour and are followed by the headache phase.
2. Vestibular Migraine:
-
- Involves vestibular symptoms affecting balance and coordination.
- Symptoms may include vertigo (a spinning sensation), dizziness, light-headedness, and problems with balance and spatial orientation.
- Individuals may or may not experience a headache during an episode.
3. Retinal Migraine:
-
- Rare type characterized by temporary vision loss or blindness in one eye.
- Vision loss typically lasts less than an hour but can be accompanied by a mild headache.
- It is essential to rule out other causes of vision loss, as it can indicate more severe underlying conditions.
4. Chronic Migraine:
-
- Defined as experiencing a headache on 15 or more days per month for at least three months, with at least eight of those headaches being migraines.
- Chronic migraines can significantly impact daily functioning and require specialized treatment approach.

5. Menstrual Migraine:
-
- Occur in women around the time of their menstrual cycle.
- Typically associated with hormonal fluctuations.
- Symptoms and triggers may vary, and hormonal management strategies can be implemented.

❖ Following are ten essential healthy tips for managing migraines and regaining control over your life.
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule : Sleep plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being, and it can significantly impact migraine frequency and severity. Aim to maintain a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Create a relaxing bedtime routine that promotes better sleep, such as avoiding electronic devices before bed, keeping your bedroom cool and dark, and practising relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Stay Hydrated : Dehydration is a common trigger for migraines, so it’s important to stay well-hydrated throughout the day. Make sure to drink an adequate amount of water and avoid sugary or caffeinated beverages that can contribute to dehydration. Keep a water bottle with you at all times, set reminders to drink water regularly, and include hydrating foods in your diet, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and leafy greens.
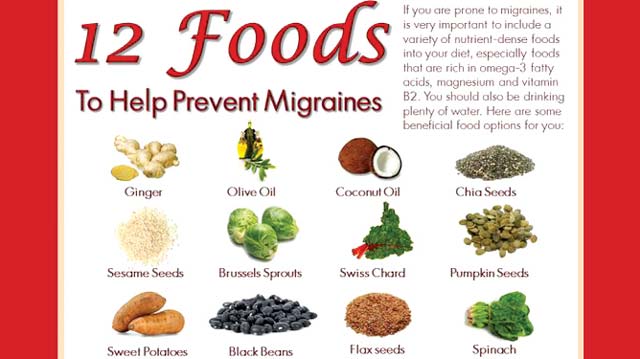
3. Follow a Balanced Diet : A healthy, well-balanced diet can play a significant role in managing migraines. Avoid trigger foods such as processed meats, aged cheeses, caffeine, and alcohol. Instead, focus on consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporate foods that are high in magnesium, such as spinach, almonds, and avocados, as this mineral has been shown to help reduce migraine frequency. Adopting a balanced diet is an important aspect of managing migraines. While dietary triggers can vary from person to person, establishing a healthy eating pattern can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
4. Practice Stress Management Techniques : Stress is a common trigger for migraines, so incorporating stress management techniques into your daily routine can be highly beneficial. Explore relaxation techniques like yoga, tai chi, or meditation. Find activities that help you unwind and reduce stress, such as engaging in hobbies, spending time in nature, or practising deep breathing exercises. Regular exercise can also help alleviate stress, so aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week.
5. Identify and Avoid Triggers : Every individual’s migraine triggers may vary, so it’s important to identify your personal triggers and take steps to avoid them. Keep a headache diary to track your symptoms and potential triggers such as certain foods, environmental factors (bright lights, strong smells), hormonal changes, or specific stress. Once you identify your triggers, make a conscious effort to avoid or minimize exposure to them to reduce the likelihood of migraines.
6. Maintain a Regular Exercise Routine : Regular exercise is not only beneficial for overall health but can also help reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines. Engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling can improve circulation, release endorphins, and reduce stress levels. However, it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity to avoid triggering a migraine. Consult with your healthcare professional to determine the best exercise routine for you. Regular exercise is a valuable component of a healthy lifestyle and can play a crucial role in managing migraines. While intense physical activity may trigger migraines in some individuals, a well-planned and consistent exercise routine can actually help reduce the frequency and severity of these debilitating headaches.
7. Create a Calm Environment : A calm and soothing environment can provide relief during a migraine attack and help prevent them from occurring. Dim the lights, reduce noise levels, and find a quiet space where you can relax and rest when a migraine strikes. When a migraine strikes, finding a calm and soothing environment can be incredibly beneficial in alleviating symptoms and promoting relief. Creating a calming environment involves setting up a space that is conducive to relaxation, minimizing sensory triggers, and providing a peaceful atmosphere.
❖ Conclusion:
Understanding the classification and types of migraines is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management. Whether it’s migraines with or without aura, hemiplegic migraines, vestibular migraines, retinal migraines, chronic migraines, or menstrual migraines, each type presents unique characteristics and considerations. Seeking medical advice and guidance from healthcare professionals is vital for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications to effectively manage migraines and improve quality of life.
Living with migraines can be challenging, but by implementing healthy tips for managing migraines, individuals can take control of their condition and improve their quality of life.
“HEALTH IS WEALTH”

