In the complex fabric of healthcare, where each intervention aims to enhance lives, the pivotal role of pharmacovigilance takes center stage. Far beyond a regulatory necessity, this specialized field stands as a dynamic and indispensable component in the ongoing commitment to ensuring the safety of pharmaceutical products. This blog delves into the intricacies of pharmacovigilance, unraveling its nuanced mechanisms, real-world impact, and the constant vigilance necessary to secure public health.
Pharmacovigilance, a cornerstone of healthcare, comprises the science and activities focused on detecting, assessing, understanding, and preventing adverse effects or any other issues related to drugs. It functions as a system for monitoring the safety of medicinal products post-market approval, ensuring that the benefits of a drug outweigh its risks. Its crucial role lies in safeguarding public health by identifying and mitigating potential harm associated with pharmaceuticals. The primary objective of pharmacovigilance is to collect and analyze information on the safety of medicines, enabling regulatory authorities, healthcare professionals, and pharmaceutical companies to make informed decisions regarding drug use. With the pharmaceutical landscape continually evolving, the importance of vigilant oversight through pharmacovigilance cannot be overstated.
One of the key aspects of pharmacovigilance is adverse drug reaction (ADR) monitoring. Adverse drug reactions encompass any harmful or unintended responses to a medicinal product and can range from mild side effects to severe, life-threatening events. Pharmacovigilance systems are designed to detect and assess these reactions, ensuring that potential risks are promptly identified and addressed. Through the collection of real-world data, pharmacovigilance contributes to an evolving understanding of a drug’s safety profile, allowing for adjustments in treatment guidelines and regulatory decisions. The pharmacovigilance process begins with the reporting of adverse events.
Healthcare professionals, patients, and even pharmaceutical companies play crucial roles in this aspect. Robust reporting systems facilitate the timely collection of data, providing a comprehensive view of a drug’s safety profile in diverse patient populations. Regulatory agencies across the globe, including entities like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), heavily depend on this data to make well-informed decisions regarding drug approvals, alterations in labeling, and even withdrawals from the market. An illustrative instance showcasing the effectiveness of pharmacovigilance occurred in the 1960s with the identification of unforeseen adverse events linked to the drug thalidomide. Initially prescribed to pregnant women as a sedative and anti-nausea medication, thalidomide resulted in a significant surge in birth defects. The tragic aftermath of thalidomide underscores the pivotal role of pharmacovigilance in averting such incidents and ensuring the safety and efficacy of drugs in the market.
With the pharmaceutical landscape continually progressing through the introduction of novel therapies, biologics, and vaccines, the role of pharmacovigilance has grown increasingly intricate. The advent of personalized medicine and innovative treatment approaches demands a flexible and vigilant pharmacovigilance framework. This involves the integration of advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and real-world evidence to enhance the detection and comprehension of potential risks. Moreover, global collaboration within the realm of pharmacovigilance is paramount. Adverse events may manifest in one region but not in others, and aggregating international data allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of a drug’s safety profile. Initiatives such as the World Health Organization’s Global Individual Case Safety Reports database play a vital role in fostering information sharing and coordination among regulatory agencies worldwide.
I. Defining Pharmacovigilance: A Guardrail for Patient Safety
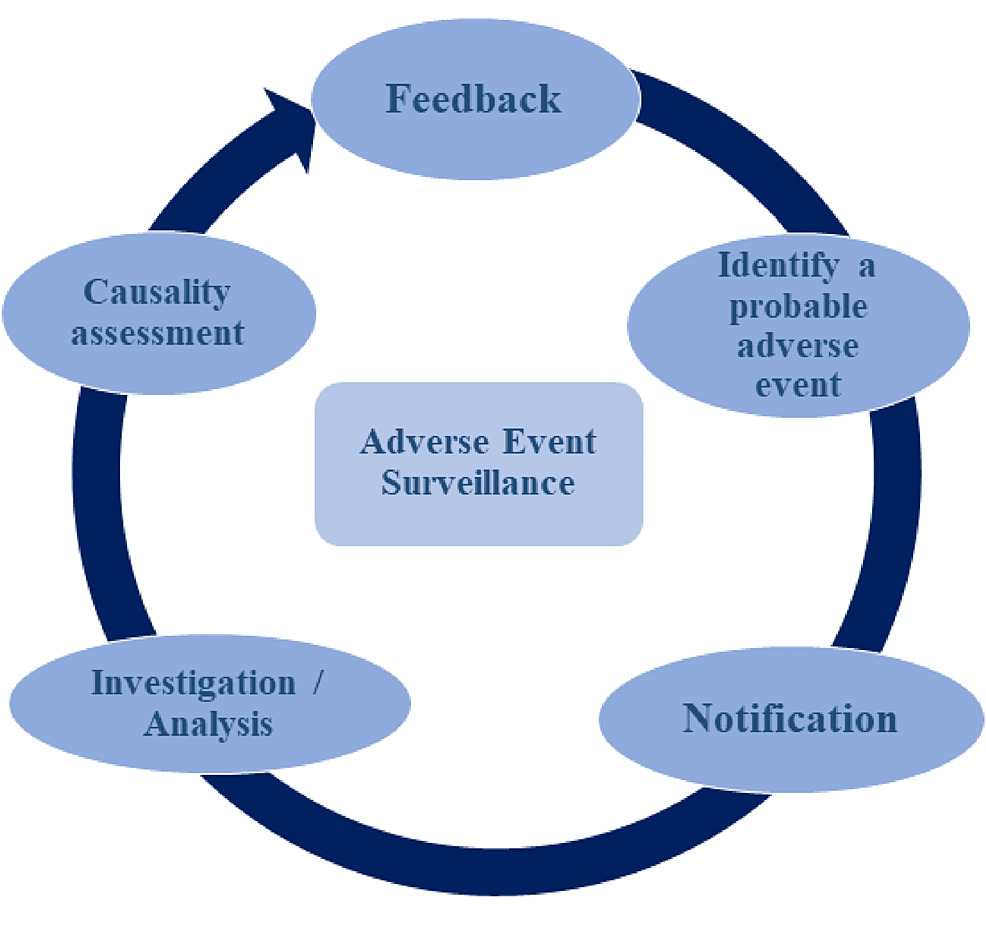
❖ Pharmacovigilance at a Glance:
Pharmacovigilance, often abbreviated as PV, encompasses the science and procedures focused on recognizing, evaluating, understanding, and averting adverse effects or any other concerns associated with drugs. This discipline employs a proactive approach to observe and evaluate the safety aspects of medications throughout their complete life cycle — extending from pre-market approval to post-marketing surveillance.
II. Navigating the Pharmacovigilance Landscape: Key Components
1. Adverse Event Reporting: The First Line of Defense
At the core of pharmacovigilance lies the systematic collection and analysis of adverse event reports. These reports, which detail any untoward medical occurrences associated with medication use, serve as the foundation for identifying potential safety issues.
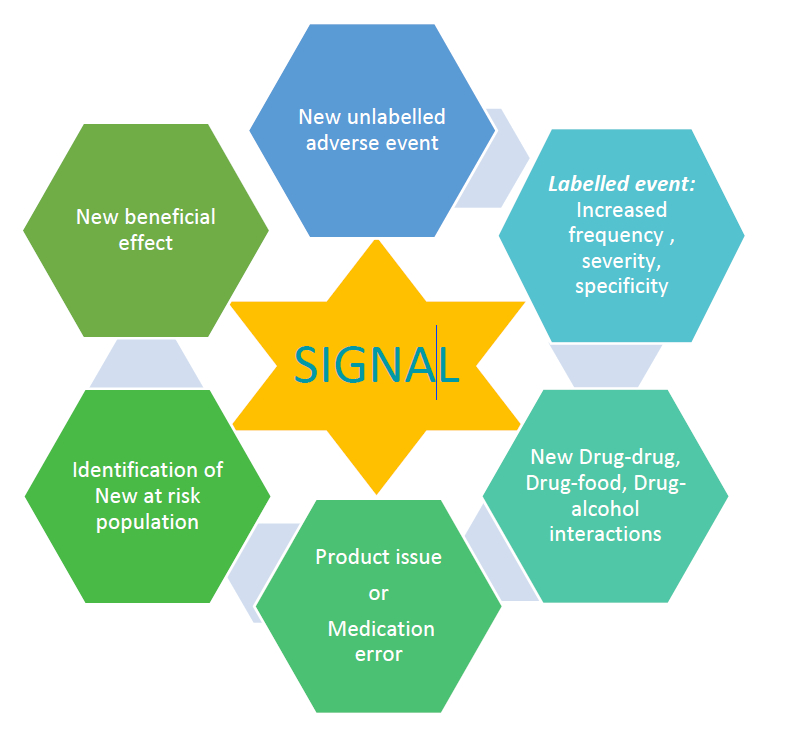
2. Signal Detection and Evaluation: Unraveling Patterns
Signal detection involves identifying patterns or trends in adverse event data that may indicate a potential safety issue. Once a signal is detected, a meticulous evaluation process commences, considering factors such as patient demographics and the overall risk-benefit profile of the drug.
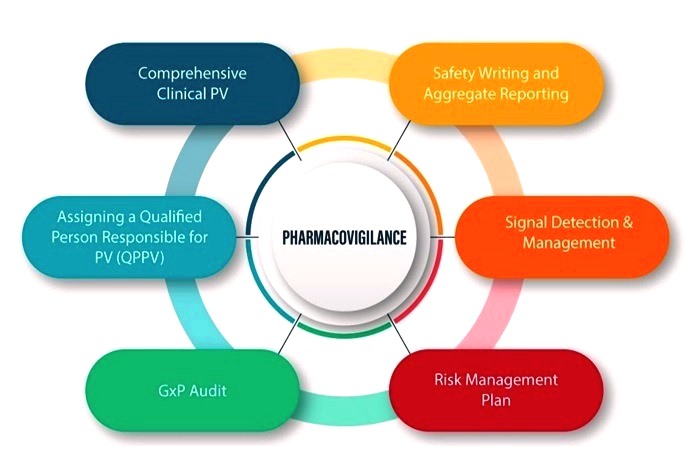
3. Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies: Proactive Safeguards
Responding to identified risks, pharmacovigilance professionals collaborate on the development and implementation of risk management plans. These plans aim to mitigate risks and ensure that the benefits of medication outweigh its potential harms.
4. Post-Marketing Surveillance: Beyond Approval
Pharmacovigilance extends its watchful gaze beyond the initial approval of medications. Post-marketing surveillance involves continuous monitoring of drugs once they are available to the public, allowing for the detection of rare or long-term adverse effects.
III. Pharmacovigilance in Action: Real-Life Examples
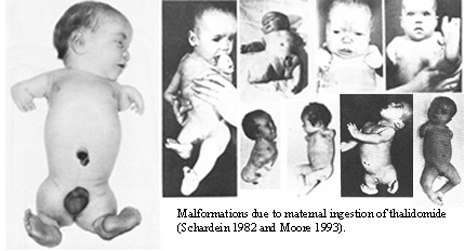
1. Thalidomide Tragedy: A Catalyst for Change
The thalidomide tragedy of the 1950s and 1960s serves as a poignant reminder of the critical need for pharmacovigilance. Marketed as a treatment for morning sickness, thalidomide led to severe birth defects. This catastrophic event spurred the establishment of pharmacovigilance systems worldwide.
2. Vioxx and Cardiovascular Risks: A Timely Intervention
The pain reliever Vioxx faced scrutiny in the early 2000s when evidence linked its use to an increased risk of cardiovascular events. The subsequent withdrawal of Vioxx from the market highlighted the role of pharmacovigilance in identifying and addressing safety concerns even after a drug’s approval.
3. Pandemrix and Narcolepsy Concerns: Unraveling Complexities
The H1N1 influenza vaccine Pandemrix faced scrutiny when reports emerged of an increased risk of narcolepsy, particularly in children and adolescents. Pharmacovigilance played a pivotal role in investigating these reports, leading to regulatory actions and a reevaluation of the vaccine’s risk-benefit profile.
IV. Challenges and Innovations in Pharmacovigilance
1. Underreporting and Data Quality: Addressing the Gaps
Underreporting of adverse events remains a persistent challenge in pharmacovigilance. Healthcare professionals may be unaware of reporting systems, or they may hesitate due to concerns about causality. Addressing this challenge requires ongoing education and efforts to streamline reporting processes.
2. Big Data and Advanced Analytics: A Technological Revolution
The advent of big data and advanced analytics has revolutionized pharmacovigilance. The ability to analyse vast datasets in real-time allows for more rapid detection of potential safety signals. Machine learning algorithms and natural language processing enhance the efficiency and accuracy of signal detection and evaluation.
3. Global Collaboration and Information Sharing: Strengthening Networks
Pharmacovigilance is a global endeavor that relies on collaboration and information sharing among regulatory agencies, healthcare professionals, and pharmaceutical companies. Initiatives like the World Health Organization’s Global Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs) program facilitate the exchange of pharmacovigilance data on a global scale.
V. The Future of Pharmacovigilance: Emerging Trends
1. Patient-Centric Pharmacovigilance: Integrating Experiences
The inclusion of patient perspectives in pharmacovigilance is gaining prominence. Patient-reported outcomes and experiences providing valuable insights into the real-world impact of medications, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of drug safety.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics: A Technological Leap
Artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics are poised to play an increasingly significant role in pharmacovigilance. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and predicting potential safety issues, allowing for proactive risk management.
3. Digital Health Technologies: Real-Time Insights
The rise of digital health technologies, including mobile health apps and wearable devices, offers new avenues for pharmacovigilance. Real-time data from these sources can contribute to the early detection of adverse events and enhance the overall surveillance of medication safety.
❖ Conclusion: Safeguarding Tomorrow’s Health Today
In conclusion, pharmacovigilance serves as a vigilant guardian of public health, diligently assessing and managing potential risks associated with medications. Through systematic monitoring, rigorous evaluation, and proactive risk management, pharmacovigilance professionals at institutions like IIMT University contribute significantly to the continual enhancement of pharmaceutical product safety. As we welcome emerging technologies and foster collaborative approaches, the future of pharmacovigilance holds the promise of even more effective and patient-centric drug safety practices.
IIMT University, recognized as the best placement pharmacy university in UP, plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape of pharmacovigilance through its commitment to excellence in education and research. The institution’s emphasis on global standards and advanced methodologies aligns seamlessly with the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring the well-being of individuals and communities by prioritizing the safety and efficacy of medications. In the ever-evolving healthcare landscape, the integral force of vigilance upheld by pharmacovigilance, particularly in institutions like IIMT University, remains a cornerstone. This commitment not only assures that the benefits of medications far outweigh their potential risks but also reinforces the trust patients can place in the safety and efficacy of the treatments they receive. As a beacon in pharmacy education, it continues to contribute significantly to the present and future of healthcare by safeguarding public well-being and maintaining the highest standards of pharmaceutical education and practice.
To learn more about pharmacovigilance, click here:
Author: Miss. Mansi,
Assistant Professor, SoPS